Volumez
on Azure
Volumez is a next-generation data service for Azure that provides higher IOPS and lower latency than Azure Disk Storage by connecting application servers directly to ultra-low latency Azure ephemeral NVMe media.
DevOps and platform engineers use Volumez declarative interface to define an application’s storage needs, and Volumez orchestrates a pure Linux data path on the target application server or AKS worker node with blazing fast performance and enterprise-grade data services including lightning-fast snapshots and multi-zone resilience.
Workloads
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Virtual Machine Database Servers
AI/ML on Azure
How it works
Azure offers two categories of block storage: Azure Disk Storage (managed) and local NVMe disks (unmanaged). Local media provides direct access to raw NVMe media, which deliver exceptional throughput and latency, but the media are ephemeral and include no data services such as RAID and snapshots. Azure Disk Storage is fully featured software-defined storage managed by Microsoft that provides data services and zonal and regional resilience.
Volumez allows customers to access the exceptional price-performance of local disks by composing a pure Linux data path on application servers that stores data directly on distributed slices of local NVMe media. Volumez recommends L8as v3 instances for local NVMe disks
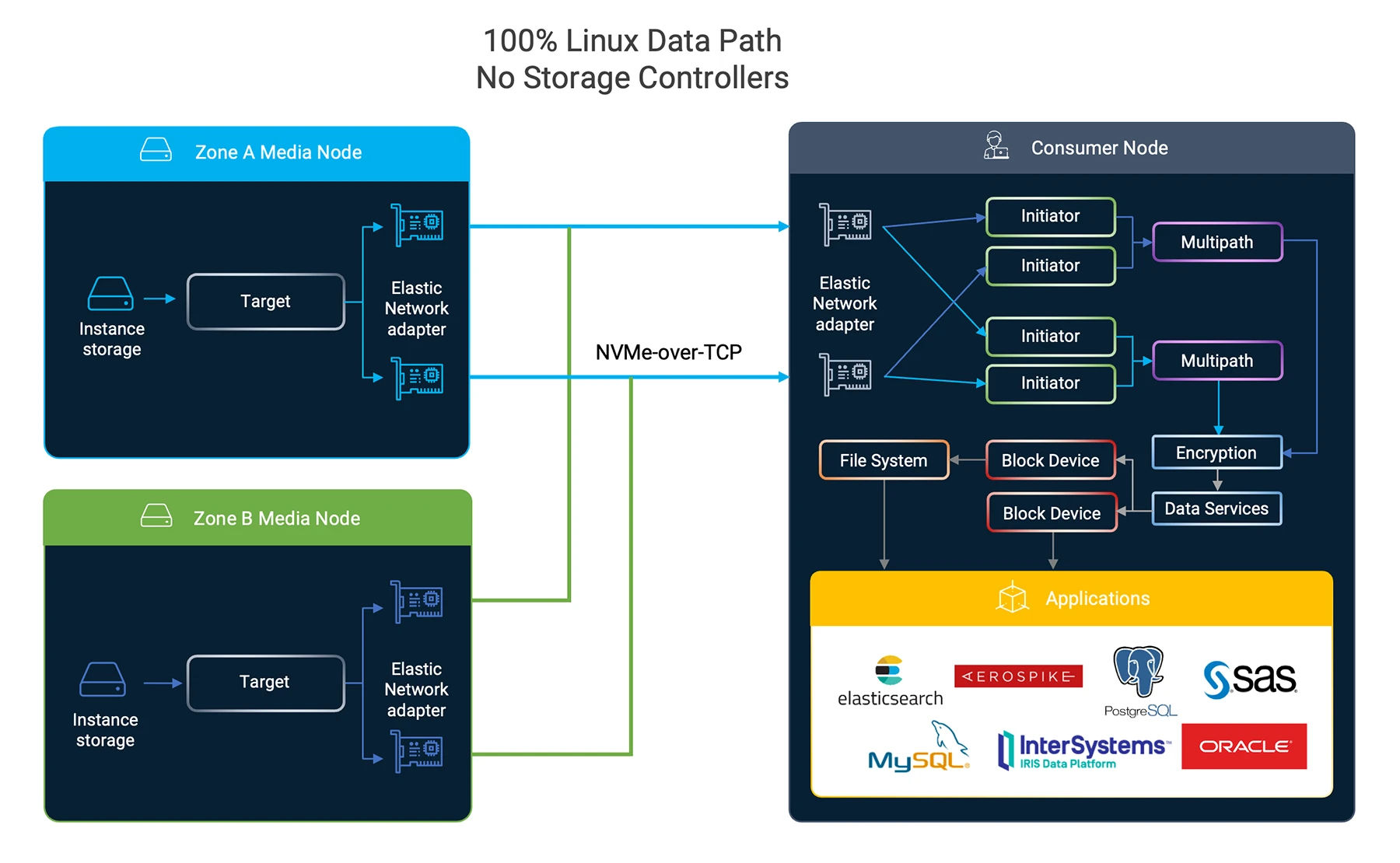
Volumez provides enterprise-grade data services including snapshots, encryption, and multi-zone resilience using a pure Linux data path. Attaching a volume to an instance requires simply choosing the volume, node name (instance), and mount point.